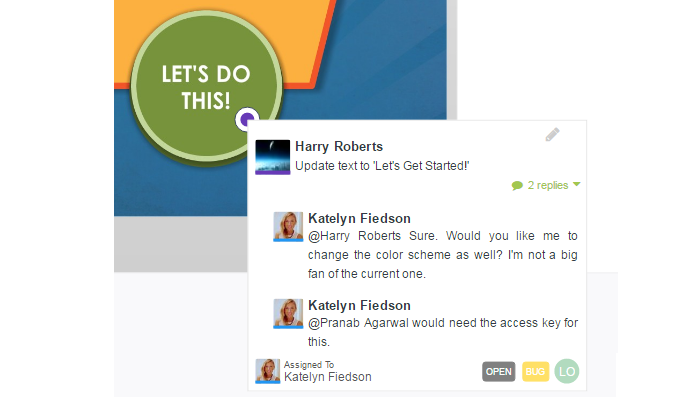
eLearning Quality Assurance Checklist with use cases and examples
04 Aug

Table of Contents
ToggleeLearning quality assurance is the final and most important process in the eLearning development process. Quality Assurance ensures that you publish a defect free eLearning course. Additionally, eLearning QA improves the learners experience and leaves a lasting experience on the learner.
However, eLearning quality assurance is a complex process as there are numerous things reviewers and testers need to check. Moreover, keeping all the QA check in mind is nearly impossible. So it’s important to use an eLearning quality assurance checklist while doing the QA.
That’s why we’ve created a comprehensive QA checklist which you can download for free.
For now let’s discuss some examples related to eLearning QA review. All the assessments are categorized in segments based on the type of element to be tested.
eLearning content development quality assurance testing checklist
1. Instructional Content – Using learning and instructional theory to ensure the quality of instruction
2. Grammar and Typography – Testing related to fonts, grammar rules, spellings, and consistency in brand styles
3. Visuals of the online content – Graphics and Images – Assessment related to Effective use of graphics and visual to enhance the experience of eLearning content
4. Audio, Voice over, and Music – Assessment related to audio, voiceover, and background music for enhancing effectiveness of eLearning
5. Course Navigation – Testing navigation of course content, best practices for navigation
6. Interactivity – Testing the interaction of various features and functions within the course.
7. Quiz and Assessment – Testing the quality of quizzes and scoring users, also some best practice mentioned.
8. Technology – Assessment of cross-browser compatibility, LMS compatibility, etc.
9. Accessibility Testing – Assess whether the course is compliant to be used by users with any kind of disability.
[Free Checklist]
eLearning Quality Assurance Checklist
Grab your free copy of the eLearning QA checklist and streamline your QA processes.
DownloadInstructional Content (Questions related to course content only)
eLearning quality assurance is not just about proofreading. It’s also about ensuring you arrange all modules and lessons in the correct sequence. Additionally, you need to provide proper instructions regarding how users will take the course. This allows the learner to understand the index and navigation of the course so they do not feel lost. This is especially necessary if the online course will be self taught.
So for instructional content, here’s what you need to check:
1. Content is accurate:
Ensure every lesson and module is labelled correctly and grouped within correct modules. All of these modules should be sequentially listed in nested format in correct order. This allows the learner to look at the whole course in one go.
2. Content is sequenced logically:
Every lesson and module of an online course should be logically sequenced. For example, for every module/lesson, the introduction should come as the first chapter and not last. Similarly all quizzes and tests should appear only once the relevant information has been taught.
Additionally, for the content taught inside each lesson, put them in order – starting from basics to complex ideas. Furthermore, while planning the sequence, keep yourself in the shoes of the learner and think as though they don’t know anything about the subject. Then, consider where they would want to start their learning.
3. Instruction to participate in the course:
Instructions are crucial not only in online courses. Generally, every product or service comes with instructional guides or user manuals. These resources enables the learner or user to know how to get the most out of the online course, how to navigate, take quizzes, fill information, and interact with other elements of the course.
If the course is going to have tests and exams at the end then let users know how to take the quiz, how to mark answers, how many attempts they will get, what’s the time limit etc.
[Free Checklist]
eLearning Quality Assurance Checklist
Grab your free copy of the eLearning QA checklist and streamline your QA processes.
DownloadGrammar and Typography
Examining your content for just typographical mistakes is not enough. A thorough grammar check should include checking all the below points.
Missing titles:
Check to ensure all the headers and titles are present. The title should be big and bold and should be clearly identifiable as a header/title.
Missing punctuations:
Not having punctuation in the right place in a sentence can possibly change the meaning of that sentence. (You sure don’t want that to happen) So ensure the punctuations are placed correctly and consistently. Some of the common punctuations used are full stops or periods, comma, colon, semicolon, question mark, exclamation, brackets, braces, apostrophe, hyphen, quotation marks.
Text positioning:
Consistently positioning text is important especially when there are visual graphics involved. For example, if there are multiple images on a slide and the text is spilled all over the place, this can confuse the learner as to what content is related to which visual and wrong information can be perceived by the learner.
Spelling mistakes:
The most common of all mistakes in grammar that we’re all guilty of is spelling mistakes. This is very common but can change the meaning of the sentence completely. For example, expect and accept might sound similar and look similar but have completely different meanings. There are some words that are spelled the same but have different meanings based on the context. These are homonyms. For example, book, which refers to a book that can be read, but the same exact word also means the act of making a reservation. That’s how English can be tricky sometimes.
Content review: Missing acronym definitions:
There are certain words made from the initial letter of other words to put forward a set of words in a few letters. For example ADDIE – which stands for Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. Now if you belong to the eLearning industry you would know this. But someone reading ADDIE for the first time will be completely clueless about what it means. So make sure that the acronyms are defined.
Casing of words:
Casing of words refers to how uppercase (capital letters) and lowercase (small letters) letters are used throughout your content. Maintaining consistent letter casing ensures clarity and professionalism while enhancing readability.
For headings, Title Case is ideal, where major words are capitalized (e.g., “Best Practices for eLearning QA”). In body text, adopt sentence case, where only the first letter of the sentence and proper nouns are capitalized.
💡 Use uppercase letters sparingly, mainly for acronyms like LMS or SCORM or to emphasize critical points. Additionally, try to adhere to a style guide to ensure uniformity across all content.
Missing/ broken links:
This is not exactly a grammar check but it makes a part of text so is included in this section. Many times for additional reading or reference we add links to external sources. Make sure these links are not broken. Not just the external links but other internal links pointing to different modules or lessons, or links to downloadables etc.
So ensure to check all links point to the right resources.
Visual of the Online Content - Graphics and Images
The next important element to check after checking typography and grammar is visual, graphics, etc. Visuals bring life to the plain boring text based content. It is scientifically proven that visual aids in any form of learning.
Therefore, it is important that the eLearning content uses enough visual and graphics to explain an idea. But you also need to check the visuals for the following:
Improve Your Visual Review Process with zipBoard
Start your free trial or book a demo today so that we can create a tailored solution for you.
Book DemoStart Free TrialTurn on audio 👆
Brand/design style guide:
Let’s say your brand uses bright and positive colors, but your online course has a very bold and dark color scheme. Moreover how about using comic style fonts for a course on a subject related to project management? People would make faces, because it would look too odd and their brains might have a hard time absorbing that content made by your company and for that particular subject.
This is why when creating a course, it’s important to ensure you follow the company’s brand style guide. So during the eLearning quality assurance process, check that the eLearning course content is consistent with the brand style guide.
Colors Discrepancy:
Every color represents a different emotion and can be perceived in a certain way by the human brain. For example try visualizing a yes tick mark in red color and a cross reject mark in green color. Doesn’t sound about right, correct?
Similarly for almost all colors there is a certain perception that we have. Try to make sure the right colors are used.
Copyright / Logo consistency throughout the course:
A logo design in general acts as the face of the business and communicates information about your business. Copyright, on the other hand, displays the owner who has the exclusive rights to reproduce, or distribute the content.
Both of these are necessary from the perspective of branding. Include the logo and copyright consistently throughout the course. Make sure it looks similar in all places where they are displayed.
Visual details/confusions (graph, charts and their resolutions are clearly seen – High Res Graphics):
Let’s consider the example of a project management related course. One lesson is about how to prepare project timelines. Now, this would have numbers and text mentioned in the graphics but because the graphic is not high resolution, the learner is unable to figure out what is being taught. All the learner sees are some blurry images with lines and unidentifiable symbols (which actually are numbers and symbols).
This check is also applicable in scenarios where how to use a tool is being taught and the video or images is not clear. It would be so hard for a learner to realize what button to click and what information to look for, where to look for it, how it looks, etc. Therefore, use visuals that show every detail that you intend to show to the online learners. Visual can be images, charts, graphics, videos and GIFs.
Appropriate Graphics as per audience (as per approved in the storyboard):
This might not be applicable in every instance. But this check is mainly with regards to any sensitive visual that can have a negative impact on learners. This check can be based on the age group of learners, gender of learners or ethnicity of learners.
For example an online course created for kids in the age group of 5-10 yrs having images that are classified as adult only. Or a course created for women empowerment containing visuals that are degrading women in certain ways and can harm the sentiments of females.
Also avoid using any other branded images without having proper license to use those, as such visuals are subject to copyright and can attract legal issues.
Visual fade in and fade out as per storyboard:
As the name suggests this is usually a bug that can be found during transitions of images, animations or videos. For example a visual is fading away but the voice over is playing without pause and before the next visual fades in the audio and visual has gone out of sync.
Another example: let’s say a video starts with a fade in effect but due to bad timing of fade in, the learner missed almost the first 30 seconds of the video where a graph was presented.
💡 Check fade in and fade out timings, sync with content or audio.
Tabs / UI elements:
Tabs and UI elements assist users to navigate through the online course. While checking these elements see if all tabs are properly labelled. Also check if icons are added and if those are correct ones.
For example, when you hover on a particular element, does the cursor change to a click icon if that was the intention? Also, was there any additional feature like “hover over to change color” that was agreed at the time of planning? If so, check to ensure that is present and functions accordingly.
Incorrect display / Wrong information displayed for a specific scenario:
This refers to scenarios where the visual might differ from the content in question and vice versa. For example, if the topic under discussion is about data and statistics, the visual to accompany this information should be a chart or graph but instead, the course creators place some other images. Check that and rectify or prompt the appropriate stakeholder.
Accessibility:
eLearning courses should be accessible by people of all abilities and disabilities. So conduct accessibility tests to ensure training and compliance programs are more effective.
Language transition:
Proper transition of language provides great cohesion and shows the relation between two concepts. Check if the language used in the course can be easily adapted by non native speakers of that language. Language transition helps in better communication of the concept to the learner.
Overall formatting of the docs, transcripts, subtitles, any text-based assets as per brand style guide:
Consider starting a course with slides completely filled with text with no formatting whatsoever. It would look bizarre and you would have no clue what relates to what. Moreover, it is visually exhausting to see a screen filled with text all over the place.
Therefore ensure the formatting of the documents, slides, PDFs and any other assets of the content is great.
White space between elements is as per the style guide:
Having too much white space can give less information and having very less white space would make it difficult for the learner to focus. Therefore keep this optimal and discuss this with your client in advance. Basis of that makes sure every piece of the online course has blank space as is approved.
Mobile view is responsive:
It is usually advisable that learners take eLearning courses on desktop or laptops to make the learning process more seamless and effective. However, there can be numerous instances where the learner would want to access the course from their smartphone.
For example, while traveling a learner might want to go through a few modules to make good use of time. It’s therefore essential to ensure your eLearning course is responsive to the screen size from which the users are accessing the course.
Missing icons:
This is another common error. Sometimes, icons are misplaced or not placed at all. Maybe the course creators and other stakeholders decided to add such icons at a later stage or that the icon design was separate from the main course creation. Consequently, they team may have forgotten to add them, which can lead to missing icons in the content, online course player, or navigation menu elements/buttons, etc.
Incorrect / irrelevant icons:
Incorrect icons are kind of similar to the previous point except an icon was placed but it is irrelevant. There is a possibility that while creating a module the required icon was not available but in order to reserve the spot a different icon was used to be changed later. Check for these inconsistencies and draw the attention of relevant stakeholders during the eLearning QA process.
Text and Icon alignment:
Alignment in general makes a huge impact in the overall look and feel of any digital content. Text and icon should be aligned so that they look centered and in sync with each other. If they’re not aligned well, learners may assume A icon is displayed for B point instead of A, and this can lead to huge confusions.
Line breaks in slides:
Line breaks are important to let learners know where a particular piece of content ends and from where a new topic will start. Without a line break the user may assume that the topic is continued in the next lesson and maybe the next chapter is talking about something totally different then the previous lesson. This would leave the user confused and they would waste time trying to relate the two topics.
Smooth Animation transition:
Everyone likes to learn from an online course which has a smooth flow of information. If you start bombarding information directly without a smooth animation transition, your course would look too packed with information and the learner might find it difficult to grasp the information.
Blank screen:
Make sure there are no blank screens during slide changes, animation transitions, questions/answer submission. For example a learner submits answers for a quiz and then the screen goes blank; what will you expect the user to do in such a situation? Nothing. And that can be very annoying.
Delay in showing elements:
This is somewhat similar to the previous point. However instead of nothing showing on the screen, it takes a long time to show the next slide, for example. Meanwhile it’s possible the learners feel nothing is happening and can go back or try to refresh or do some action which can break the flow of learning. Consequently, the learner might have to restart the module or even the quiz for that matter.
Missing buttons:
This is one of the worst misses an online course can have. Missing buttons could be player buttons, navigation buttons or other type of interaction buttons. For example text on screen say click this button to reveal the image and there is no button there. How frustrating that would be for a user!
Interactive button missing:
We have already covered this in the previous point. But this is added as a separate point as the chance of missing an interactive button is higher than other buttons. Why?
This is because interaction buttons would be topic and content specific and would be placed differently in different places.
Button Labels (static or hover as decided during planning/ storyboarding):
Think about this for a minute you start a course and there are 5 buttons but none of them are labelled which one would you click? That’s confusing, right? That is why it’s important to have a label on buttons so that the user knows which button they should use – and when.
Able to enlarge images and vice versa:
It is possible that the eLearning course designers used a thumbnail image in the slides.. If this is the case, the user may want to enlarge and see the details to get a good understanding of the visual. So check to see if that is possible and leave a comment to prompt the appropriate stakeholders. zipBoard makes this easy.
Ideally clicking on an image should enlarge the image, but you might have planned the interaction in a different way. Either way, the point is that the users should be able to enlarge the image. Also the enlarged image should be the high resolution version not the thumbnail version.
Order of items in a graphical image:
Ensure designed visuals have logical order of items. For example, the text on the slide says XYZ points are shown in the graphic/image in ascending order. However in the graphic/images it’s in descending order. That would completely make the information opposite of what your end goal is – which is counterproductive.
Text/graphic cut off:
Check for any text or graphics being cut off from the screen. This can happen in slides, docs, downloadable, transcripts, subtitles and in other visuals. It can also happen when the course content is not screen size responsive and some portion gets cut off in different screen sizes. To fix this you will have to do cross browser testing which we are going to discuss in further points.
[Free Checklist]
eLearning Quality Assurance Checklist
Grab your free copy of the eLearning QA checklist to learn how to streamline your QA processes.
DownloadAudio, Voiceover, and Music
It’s worth noting that audio quality is more crucial than the visual quality of any online course. Audio actually explains the complete concept. There can be a single sentence or one visual on the screen but the audio would completely explain all about that topic.
Here are the items you need to cross off your eLearning quality assurance checklist:
Quality of the audio:
This is to ensure the sound is not muffled, or that the playback is very fast or very slow. Sometimes the audio can even be very high pitched or low pitched. In either case, it would not give the learner a good learning experience. Moreover every learner might have different kinds of earphones or speakers so it’s necessary to have audio quality optimized for all kinds of devices.
Pronunciation:
We talked about bad audio quality in previous points. But let’s not forget about the accent of the language. For example, an American accent might not be easily understood by a non-native speaker. So it’s best to keep the language as neutral as possible so that learners from any ethnicity can understand the content.
No background music:
This has to do with adding background music when an important concept is being explained and there is already a voiceover in play. Also, if the background music is completely silent throughout the course it can get boring.
So make sure to check background music is only used in places where necessary and the volume is soothing and helps the learner focus. Try not to add a dance music tune as a background sound; the user might end up figuring out what song is, rather than focusing on the content in front of them.
You can take the help of GarageBand music software for adding suitable background music.
Loud background music:
Remember, one of the reasons background music is there is to keep the user engaged, and not feel blank. However, if the background music is loud, it would interfere and not let the user focus on learning.
Voice over sync:
There should be proper sync in what appears on the screen and what is being said in the voice over. Review the course as a whole with eyes open and focused on the screen to make sure the sync is correct.
Missing part of Voice Over:
There can be scenarios where either the voice over was missed to be added in a certain part of the video or slide. Or it was muted, or the voice was kept down during editing. Check if there is any missing piece of audio voice over.
Overlapping Voice Over:
This can happen when the slides were created with an audio recording and later another voice-over was also added at the time of the video editing process. See if you find any such part in the content where there is an overlapping voiceover. Mark the timing of such parts in your eLearning quality assurance report. You can use a video review and collaboration tool to give time-stamped feedback on eLearning video content.
Subtitle sync with audio:
When subtitles appear before or after the scene is completed and dialogue has been spoken, it can confuse the learner. Ideally the subtitles should appear as the topic is being explained. So ensure to check this is accurate.
Playback Speed adjustment:
Allowing this feature in a course is advisable as it allows the user to take the course at their own pace. Check if users can adjust the speed of the online course. If they can’t check if the playback speed is set to normal so that anyone can easily understand and gain knowledge from the course.
[Free Checklist]
eLearning Quality Assurance Checklist
Grab your free copy of the eLearning QA checklist to learn how to streamline your QA processes.
DownloadCourse Navigation
Slide navigation:
There are various navigation available on a slide. And you need to decide on what all navigation options you want to provide to the user. This should ideally be discussed in the planning phase. Based on the approved navigation, check if all of them are consistently used throughout the complete course.
Lesson sequence:
Check if the navigation button functions as intended to and points to the right lesson.
For the below items check what kind of navigation is approved at the time of:
Planning/storyboarding
These checks are based on what the client agreed on and approved. So while doing the eLearning content QA, you might not have to go through each of the tests mentioned in this section.
Able to go to the next lesson only by completing:
In some courses it is mandatory that the current topic is completed before moving on to take the next lesson. Check that the next button is disabled or does not function unless the current lesson is 100% completed.
Able to go to the next lesson by skipping current one:
Check whether the learner can access the next page by skipping the current content. If so, see if they can do that or not.
Able to go to the next lesson upon successful completion of a test in the current module:
Sometimes there can be quizzes and tests at the end of the course. These are at times used to evaluate and rank users and sometimes only to let the user take a quiz and see how much they have learned. Based on the purpose of the course, check if the next button is functioning as was agreed and approved during the storyboarding/planning phase.
Start the next module automatically:
Another important navigation factor is automatically starting the next module upon successful completion of the current module. See if this is agreed, and if this is consistent throughout the course.
Starts next module only upon the click “Next”:
Similar to the previous point, confirm whether the planning phase included an agreement to design the course for self-paced learning. If so, ensure the module pauses after each section is completed, allowing learners to decide whether to proceed to the next lesson immediately or take a short break before continuing.
Hover over additional info marks lets you access more information:
Include this check only if the feature (placing a small question mark or info icon in specific areas) was discussed and approved during the planning or storyboarding phase.
When users hover their mouse over these icons, they should see bite-sized additional information related to the content, button, or feature.
Stuck at certain interactions:
Identify and address issues like blank screens, missing buttons, or absent visuals that occur after completing a test or clicking on the next lesson.
These glitches disrupt the user experience and should be flagged for immediate resolution during the QA process.
Get User Feedback on Online Couses
Start your free trial and collaborate with stakeholders to improve user experience or book a demo today so that we can create a tailored solution for you.
Book DemoStart Free TrialInteractivity - Activity functions as is being advised in the course
We already talked about the buttons and their labels in the previous section. In this segment we are going to check whether the elements interact currently when the learner takes an action in the course.
Shows items at click work correctly for every lesson:
Ensure all interactive elements like images, charts, or graphics that are hidden behind buttons function correctly. For example, if the course instructs learners to click a button to reveal an image, verify that clicking the button successfully displays the content.
Additionally, ensure the mouse cursor changes to indicate the button is clickable. Address any issues where clicking produces no result.
Feedback functions or yes/no interactions functions correctly:
Engaging learners often involves asking simple YES/NO questions. Ensure these interactions work as intended. For instance:
- Clicking YES or NO should allow learners to proceed.
- If no action is taken, the course should pause until a response is given.
- Confirm this feature functions smoothly if included in the course design.
Submit buttons functions properly (eg. submit an answer, submit text):
Submit buttons play a crucial role in forms, quizzes, and tests. This button should usually do 2 things: store the data in the backend (database) and on the frontend it should show if the form/quizzes was submitted and allow the learner to move forward.
For quizzes without data storage, ensure learners receive confirmation upon submission and can continue to the next section.
Submit button logic and display of relevant information:
For inputs requiring specific data formats (e.g., numbers in a value field), ensure submit buttons validate the input. If invalid data is entered, the system should display an error message and prompt the learner to correct it before proceeding.
Other interaction was approved in the storyboarding/planning phase:
If custom interactions were approved during planning or storyboarding, ensure these are implemented as designed and function correctly.
Praising a certain behavior:
It is psychologically proven that when a person is praised for their action / behavior they show more interest and perform better. For this reason, it’s important to incorporate features that praise learners for correct actions or behavior. For instance, awarding points for correct answers or giving bonus points for perfect scores can enhance engagement and motivation. Ensure these features work as intended.
Form completion:
Forms should distinguish between mandatory and optional questions. Whenever a form is submitted the data in the form should get stored in the backend and the learners should be able to move to the next lesson.
Based on what is approved, going to the next lesson can be automatic or interaction based. Check whether all of these actions are functioning properly when a form is submitted.
Form dropdown options:
Dropdown menus should function correctly and offer relevant options. If none of the options apply, ensure there’s an “Other” option with space for custom input.
Able to pause course if needed:
For self-paced courses, ensure learners can pause without losing progress. For time-bound courses, verify that the pause function is disabled once the course starts. Use tools like zipBoard to screen record a short video to show if all the button in the player are working correctly.
Incorrect score displayed:
Check that quiz scores are displayed accurately. For instance, ensure the system shows only the most recent attempt’s score rather than a cumulative total of all attempts.
Hide/unhide player buttons functions correctly:
Verify whether the course player buttons are displayed as intended—either always visible or hidden after a set time—based on the planned design.
Go to home or main module buttons available throughout the course:
Ensure learners can navigate back to previously completed modules using “Return Home” or “Main Module” buttons. These buttons should appear on every slide and direct learners to the intended module.
Able to download files:
Learners should be able to download additional resources like transcripts, images, or templates. Verify all downloadable resources function correctly.
Locked menu:
For courses requiring sequential completion, ensure the menu is visible but locked to prevent skipping lessons out of order. You can disable certain fields based on completion of an activity.
[Free Checklist]
eLearning Quality Assurance Checklist
Grab your free copy of the eLearning QA checklist to learn how to streamline your QA processes.
DownloadQuiz and Assessment
The below points are the possible options that can be planned and finalized for the quizzes at the time of planning and storyboarding. This is self explanatory and while testing this checks see if the feature functions as intended.
Submit right answer gives you Green signal and additional information about the questions/answers.
Submit wrong answers does not let you go to the next module.
Submit wrong answers shows the right one and tell you why what you choose is wrong and lets you move forward.
Accurate score gets collected in the backend and shown to the participant – Lets say the learner attempted multiple times and had different scores every time. In this case we can either show them latest marks only or all marks segregated attempt wise.
Number of attempts to answer a question as per the storyboard – Basis of how many attempts you want to provide when somebody fails the quiz or test. Check if the learner is able to attempt that many times. And if they pass the test they should be able to move forward.
Hitting the back button during test/quiz – Ideally this should not be allowed however depending on the course test this as was planned and approved by the client.
Technology
Tested content on various browsers for compatibility (Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Chrome.):
Ensure your course functions seamlessly across different browsers, such as Google Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and Internet Explorer. For instance, a course may display perfectly on Google Chrome on a desktop but encounter issues like cut-off visuals or malfunctioning features on Safari on a Mac.
Use tools like zipBoard to test your content on different browsers and screen resolutions to verify compatibility and address any inconsistencies.
Mouse clicks and keyboards function smoothly:
For learners to interact effectively with the course, it’s crucial that mouse clicks and keyboard inputs function without issues. Test all actions requiring user input—such as navigation, form submissions, and quizzes—to confirm they respond accurately and consistently on various devices and operating systems.
Course content player menu functions as desired (as per applicable):
The course player menu, including essential controls like Play, Pause, Stop, Volume, Playback Speed, and Seek Bar, must function as expected. These features enhance user comfort and accessibility.
For instance, if a user needs to adjust the volume but cannot due to a faulty control, it can significantly hinder their learning experience.
Test all player menu options to ensure they work correctly and provide a user-friendly experience.
Backend tracks participant’s data accurately:
Ensure the backend system accurately tracks participant data, such as personal information, pass/fail status, scores, and any custom interactions.
Test all forms, quizzes, and activities to confirm that data is stored and retrieved correctly. Reliable tracking is essential for monitoring learner progress and generating meaningful reports.
Learning management system compatibility of the content:
Your course must be compatible with the LMS it will be hosted on. Upload the course to the LMS and review it as a learner to ensure all features—such as navigation, tracking, and interactivity—function as intended. Address any compatibility issues before rolling out the course to ensure a smooth learning experience for users.
Accessibility Testing
Now that you’ve completed all the checks for your eLearning course, there’s one final step before making it live: ensuring compliance.Compliance refers to adhering to a set of standards or rules applicable to your product—in this case, your eLearning course.
Designing the course to meet these standards simplifies the development and publishing process while ensuring a better learning experience for users.
Compliance requirements vary depending on the industry the course is designed for. For example, AICC (Aviation Industry Computer-Based Training Committee) standards were developed to address technical requirements for computer-based courses in the aviation sector. While specific industries may have their own compliance standards, this section focuses on general compliance applicable to all eLearning courses.
One crucial compliance standard is WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines), established by the World Wide Web Consortium to make online content accessible to people with disabilities. Many countries, including the U.S., have enacted laws mandating digital materials meet accessibility standards. Following WCAG ensures your course is inclusive and legally compliant. Learn more about eLearning compliance.
We’ve compiled a comprehensive list of checks, examples of potential issues, and explanations to illustrate the importance of each step and how to address them. However, eLearning is a constantly evolving field, and new challenges may emerge. We’ll strive to update this article as we encounter additional errors, issues, or standards to help you stay ahead of the curve.
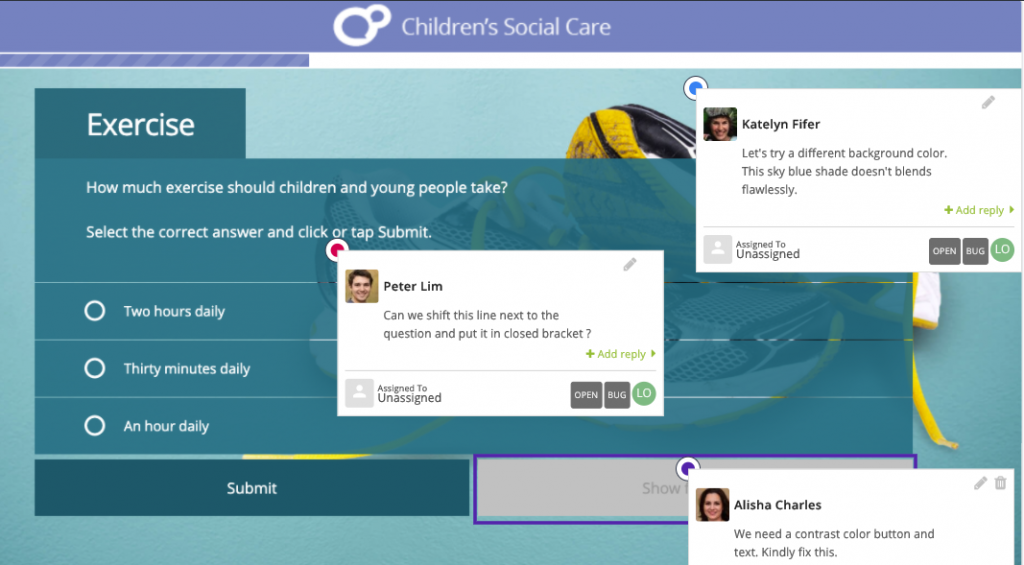
[Free Checklist]
eLearning Quality Assurance Checklist
Grab your free copy of the eLearning QA checklist to learn how to streamline your QA processes.
DownloadDisadvantages of Conducting eLearning Quality Assurance with Spreadsheets
While spreadsheets have traditionally been used for various organizational tasks, they may not be the most effective tool for conducting eLearning QA. Here are some notable disadvantages of relying on spreadsheets for this purpose:
1. Limited Collaboration: Spreadsheets are primarily designed for individual use, making it challenging for multiple team members to collaborate in real-time. This can result in communication gaps and delays in the QA process, especially when teams are geographically dispersed.
2. Version Control Issues: Maintaining version control in spreadsheets can be cumbersome. When multiple team members make edits simultaneously, it can lead to conflicting changes and data loss, making it difficult to track the history of revisions.
3. Complexity: As eLearning projects grow in complexity, so does the course QA process. Spreadsheets can become overwhelming when trying to manage a multitude of courses, modules, and testing criteria. This complexity can hinder productivity and increase the likelihood of errors.
4. Lack of Automation: Spreadsheets lack built-in automation features, which means QA testers must manually enter data and perform calculations. This can be time-consuming and increases the risk of human error.
5. Inadequate Reporting: Generating comprehensive reports from spreadsheets often requires manual effort. Without robust reporting capabilities, it becomes challenging to gain insights into the QA process and identify areas that need improvement.
6. Scalability Challenges: As your eLearning program expands, managing quality assurance in spreadsheets becomes increasingly impractical. Scaling up the process with spreadsheets may result in inefficiencies and decreased effectiveness.
zipBoard: The Content Review Tool for Effective eLearning QA
To address these disadvantages and enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your eLearning QA process, consider using zipBoard.
zipBoard is a centralized visual content review and collaboration platform designed to streamline the QA workflow. Here’s how zipBoard can benefit your eLearning projects:
1. Real-Time Collaboration: zipBoard facilitates seamless collaboration among team members, allowing them to review and provide feedback on eLearning content in real time. This eliminates communication bottlenecks and ensures faster issue resolution.
2. Contextual Feedback with Visual Review and Collaboration Tools: zipBoard provides several annotation features to help give contextual feedback on eLearning courses during the QA process. This helps ensure clarity and saves 60% of time on eLearning QA reviews – thereby leading to faster product launches.
3. Version Control: zipBoard offers version control features, ensuring that all changes and comments are tracked, making it easy to revert to previous versions if needed.
4. Simplified Complexity: With an intuitive user interface, zipBoard simplifies the management of eLearning courses, modules, and testing criteria, making it easier to collaborate with technical and non-technical stakeholders in the QA process – all in one platform.
5. Automation: zipBoard automates repetitive tasks, such as capturing screenshots and tracking changes, reducing the manual effort required during QA.
6. Comprehensive Reporting: zipBoard provides automated reporting and analytics features, enabling you to gain valuable insights into the eLearning quality assurance process, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions for improvement.
7. Scalability: As your eLearning program grows, zipBoard scales with you, ensuring that your eLearning QA process remains efficient and effective even with larger projects.
Improve Your eLearning QA Process with zipBoard
Start your free trial or book a demo today so that we can create a tailored solution for you.
Book DemoStart Free TrialReady to Improve Your Visual Review and Bug Tracking Process for eLearning QA?
Building great courses requires collaborative effort, but collaboration is only effective when teams can communicate ideas clearly and efficiently. Without seamless communication, you can lose the best ideas in translation.
That’s why visual communication is vital for every professional involved in developing online training programs. Clear, visual feedback bridges gaps and ensures everyone—designers, developers, SMEs, and clients—is on the same page.
zipBoard isn’t just an exceptional visual communication tool; it’s purpose-built to offer you and your team a complete, streamlined experience with features like:
- Sharing Feedback: Mark up and annotate directly on digital assets for clear, actionable input.
- Creating Tasks: Convert feedback into tasks effortlessly, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
- Prioritizing Tasks: Organize and prioritize your tasks to meet deadlines and align with project goals.
- Reviewing Various File Formats: Collaborate on documents, images, videos, and more in one place.
- Recording Video Feedback: Capture detailed issues or defects visually with video annotations.
With zipBoard, you can manage multiple projects involving multiple stakeholders—like SMEs and clients—seamlessly. Our cloud-based collaborative platform centralizes visual reviews, bug tracking, and client feedback management, saving your team time and effort while improving the quality of your eLearning courses.
Launch Your eLearning Courses Faster with zipBoard
Start your free trial or book a demo today so that we can create a tailored solution for you.
Book DemoStart Free TrialLook at what our customers think about zipBoard

” Zipboard has been amazing for quickly being able to point out complex or difficult to explain changes that need to be made on our website. Rather than write up a small book I can quickly use the provided tools to visually capture the problem and point, encircle, and write a note connected to the needed changes. It has saved us so much time and increased productivity. Highly recommend. “
Nathan Williams
Marketing Director at Best Practice Medicine

” The overall value comes from efficiently gathering feedback from our quality assurance team and any other stakeholders. This is very important because we want to ensure quality but at the same time, if we had to collect the feedback in another way and coalesce them, this would take time and effort that zipBoard makes easy for us. So it’s very valuable. “
John Just
KnowBe4’s Senior VP of Learning Innovation

” Implementing zipBoard into our development process has taken the team from using antiquated manual processes to an easy to use, globally accessible, online process. The application is flexible in how projects are set up and managed. zipBoards environment allows multiple projects to be set up and managed uniquely; where other tools force a specific method for everything. “
Beth Epperson
QA Manager - ELM Learning
Frequently Asked Questions
Quality assurance (QA) in eLearning ensures that digital learning content meets established standards for functionality, usability, design, and learning effectiveness. It involves systematic checks and reviews throughout the development process to detect and fix issues before launch, ensuring a high-quality learning experience.
The 4 C’s of quality assurance often refer to:
- Correctness: Ensuring the content is accurate and free of errors.
- Consistency: Maintaining uniformity in design, navigation, and instructional approach.
- Clarity: Making sure content is easy to understand and accessible to learners.
- Completeness: Ensuring all required learning components are included and function as intended.
The four key points of quality assurance in eLearning typically include:
- Content Accuracy: Verifying the correctness of instructional materials.
- Functionality: Ensuring that features like navigation, media, and quizzes work as intended.
- User Experience (UX): Checking ease of use, accessibility, and design consistency.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating how the course runs on different devices, browsers, and platforms.
The three essential QA activities in eLearning include:
- Planning: Establishing QA goals, processes, and checklists.
- Testing and Review: Conducting detailed checks for content accuracy, usability, and technical functionality.
- Reporting and Feedback: Documenting issues found, providing recommendations, and ensuring corrections are implemented.
Related Post
Recent Posts
- User-Friendly E-Learning Review Tools: Trends for Teams in 2026 February 20, 2026
- Your Digital Asset Review Workflow Is Broken (And How to Fix It) February 3, 2026
- Best Practices for Efficient Document Reviews and Collaboration December 18, 2025
- MEP Document Management: How to Streamline Reviews & Avoid Rework October 3, 2025
- What Is Online Proofing Software? And Why Content Review Breaks Without It July 11, 2025
©️ Copyright 2025 zipBoard Tech. All rights reserved.